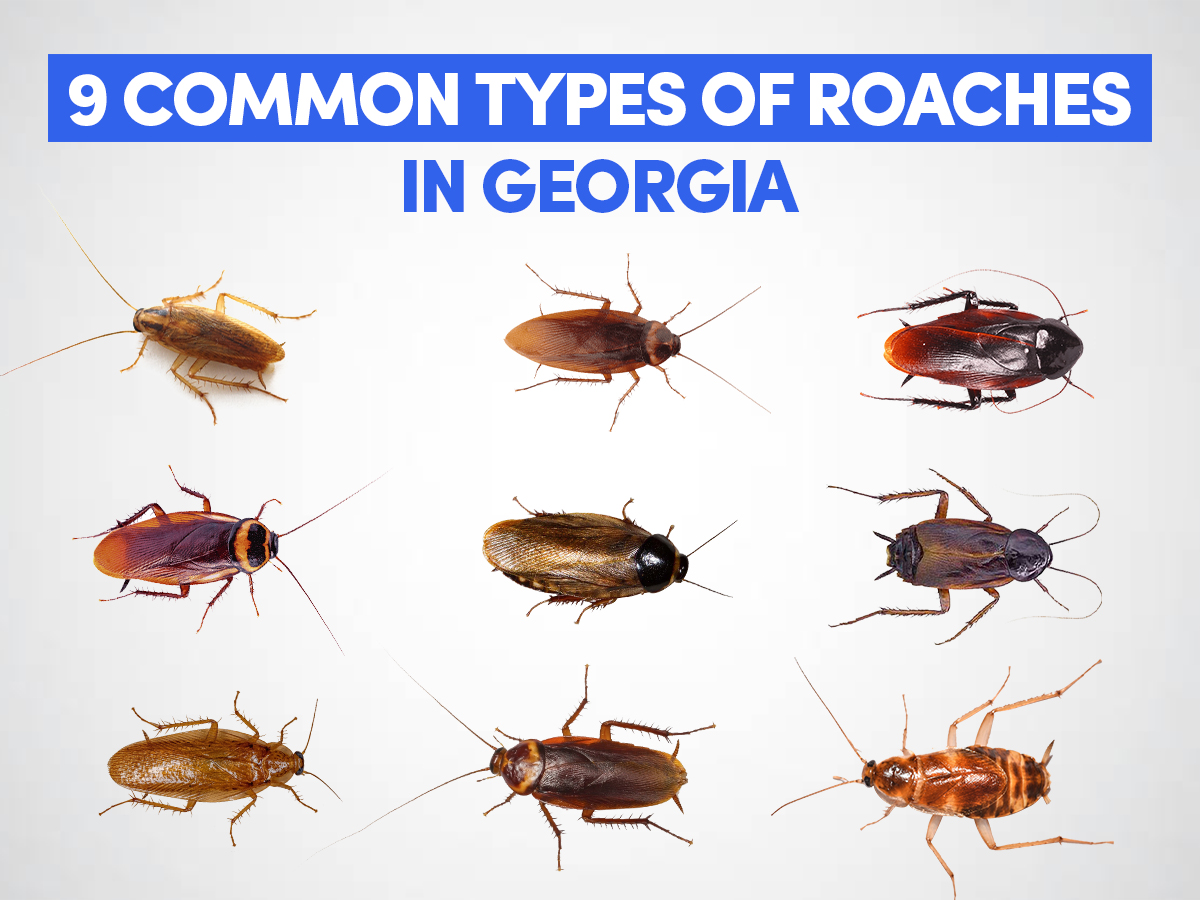
Imagine flipping on your kitchen light late at night, only to see cockroaches darting across your counter. In Georgia’s warm, humid climate, such encounters are unfortunately common. These pests are more than just a nuisance—they carry bacteria, contaminate food, and can trigger asthma and allergies.
With over 3,500 species of cockroaches worldwide, Georgia is home to several, including the quick-breeding German cockroach and the large, bold American cockroach, each presenting unique habits, behaviors, and challenges.
This guide is designed to help you identify the most common types of roaches Georgia has, understand their habits, and learn how to eliminate them. Let’s explore how to recognize, manage, and keep these Georgia roaches at bay.
Quick Comparison of Key Features of 9 Common Types of Roaches in Georgia
| Roach Type | Size | Appearance | Habitat | Behavior |
| German Cockroach | 0.5-0.6 in | Light brown with two dark brown parallel strips at back. | Kitchens, bathrooms | Fast breeders, indoors, known for contamination |
| American Cockroach | 1.5-2 in | Reddish-brown with yellowish figure-eight pattern on the back. | Sewers, basements | Occasional flier, One of the big roaches in Georgia |
| Smoky-Brown Cockroach | 1-1.5 in | Dark brown or mahogany with outer shiny body. | Outdoors, woodpiles | Strong flier, nocturnal |
| Asian Cockroach | 0.5-0.6 in | Resembles the German cockroach but slightly smaller, wings extend the body. | Prefer outdoor settings | Highly attracted to light, strong fliers |
| Australian Cockroach | 1.2-1.5 in | Reddish-brown with yellow markings on thorax and wings. | Warm, humid areas | Plant feeder, good flier |
| Surinam Cockroach | 0.75-1 in | Shiny dark brown to black body with a lighter underside. | Tropical and sub- tropical outdoor settings | Burrowing roaches, Can cause significant damage. |
| Oriental Cockroach | 1 in | Dark brown/black robust body, small wings or wingless | Damp, cool areas | Slow-moving, “water bugs” |
| Brown-Banded Cockroach | 0.5 in | Light brown with two distinct brown bands across the wings and abdomen. | Dry areas | Hides in high locations |
| Wood Cockroach | 0.75-1.25 in | Light brown with a slightly translucent body. | Outdoors, wooded areas | Not an indoor pest |
1. German Cockroach
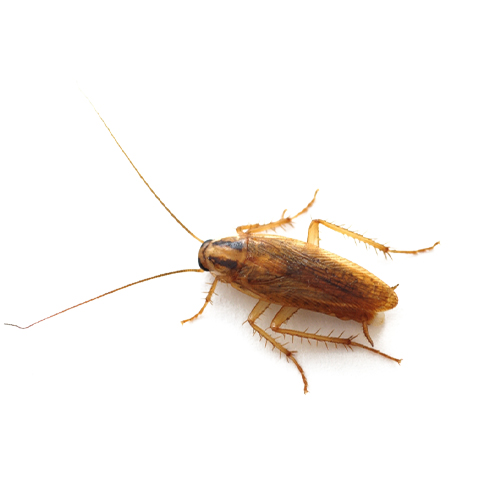

These roaches reproduce rapidly, making them difficult to control. They thrive indoors, often hiding in cracks near food and water sources. A single female can produce hundreds of offspring in a year. Known for contaminating food and spreading harmful bacteria like Salmonella and E. coli, they often require professional intervention.
- Scientific Name: Blattella germanica
- Size: 0.5 to 0.6 inches long
- Appearance: Light brown or tan with two dark parallel stripes running along the back of their heads. Wings are present, but they rarely fly.
- Habitat: They prefer warm, moist areas like kitchens, bathrooms, and food storage spaces.
- Diet: Feed on food scraps, decay, and organic matter
2. American Cockroach
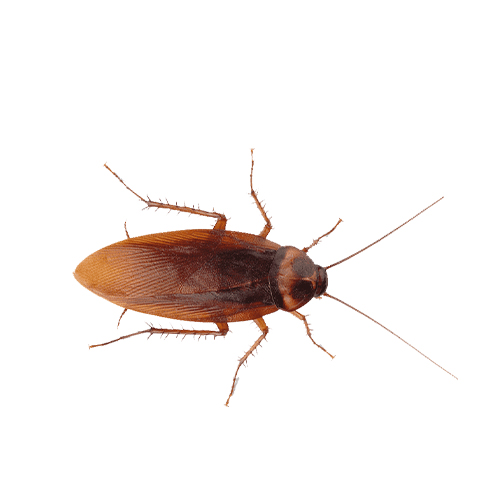

Commonly known as “palmetto bugs,” they are some of the largest roach species found in the area. American cockroaches rarely settle indoors. These pests are known for their ability to glide short distances using their wings. Thriving in Georgia’s warm and humid climate, they are a common sight in outdoor spaces.
- Scientific Name: Periplaneta americana
- Size: 1.5 to 2 inches long
- Appearance: Reddish-brown with a distinctive yellowish figure-eight pattern on the back of their heads.
- Habitat: Found in warm, damp areas like basements, sewers, and drainpipes. They may invade homes during colder weather.
- Diet: Omnivorous scavengers that feed on decaying matter, crumbs, and even paper.
3. Smoky-Brown Cockroach
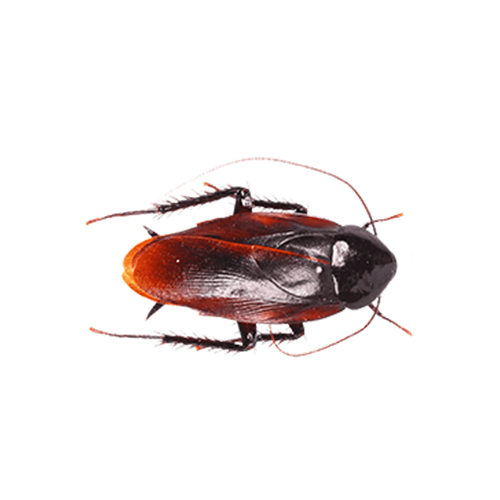

These red roaches in Georgia, are strong fliers and highly active at night. Attracted to light, they often seek out moisture and food sources. Their nocturnal habits make them a common nuisance in warm, humid environments.
- Scientific Name: Periplaneta fuliginosa
- Size: 1 to 1.5 inches long
- Appearance: Uniform dark brown or mahogany color with a shiny exoskeleton.
- Habitat: Prefers outdoor environments like woodpiles, tree bark, gardens, and gutters. They are attracted to light and may enter homes in attics during cold or rainy seasons.
- Diet: Feed on plant material, decaying organic matter, and stored food.
4. Asian Cockroach
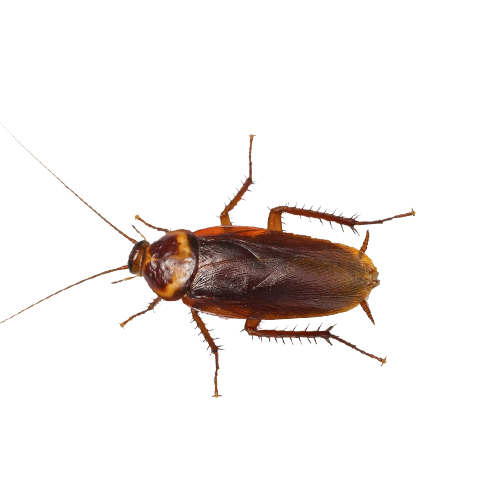

These flying roaches in Georgia are strong fliers, distinct from the smaller German cockroach. Asian cockroaches are highly attracted to light and more commonly found outdoors than indoors. These pests are most active in warm, humid environments.
- Scientific Name: Blattella asahinai
- Size: 0.5 to 0.6 inches
- Appearance: Resembles the German cockroach but slightly smaller and is lighter in color with wings that extend slightly past the body.
- Habitat: Found outdoors in shaded areas, gardens, and leaf litter but may enter homes when drawn to light. Prefer outdoor settings.
- Diet: Feed on plant matter and small insects.
5. Australian Cockroach
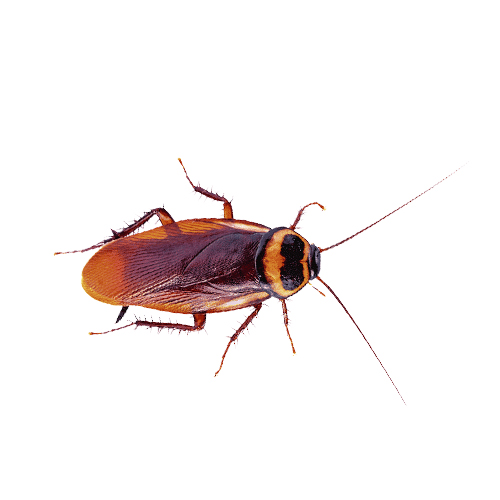

The Australian cockroach, often mistaken for a palmetto bug, is an excellent flier and one of the larger roach species. These pests are attracted to light and can invade homes in search of food and moisture.
- Scientific Name: Periplaneta australasiae
- Size: 1.2 to 1.5 inches long
- Appearance: Reddish-brown with yellow markings on the thorax and edges of the wings.
- Habitat: Found in warm, humid climates and is common in greenhouses, gardens, and tropical regions. Can invade homes through cracks and crevices.
- Diet: Primarily feeds on plant materials but can also invade homes for food.
6. Surinam Cockroach
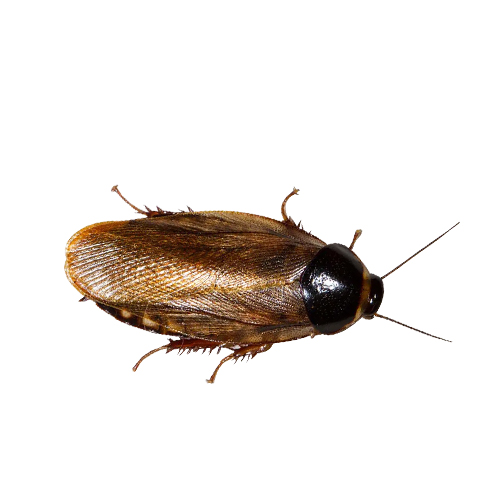

The Surinam cockroach is a burrowing pest that damages garden plants and indoor potted plants. Females reproduce parthenogenetically, allowing them to produce offspring without mating.
- Scientific Name: Pycnoscelus surinamensis
- Size: 0.75 to 1 inch
- Appearance: Dark brown to black with a shiny, smooth body with a lighter underside. Females are winged, but males are rare in the species.
- Habitat: Prefers outdoor environments like soil, leaf litter, and compost piles. Often found in tropical and subtropical areas.
- Diet: Primarily herbivorous, feeding on plant roots and decaying vegetation.
7. Oriental Cockroach
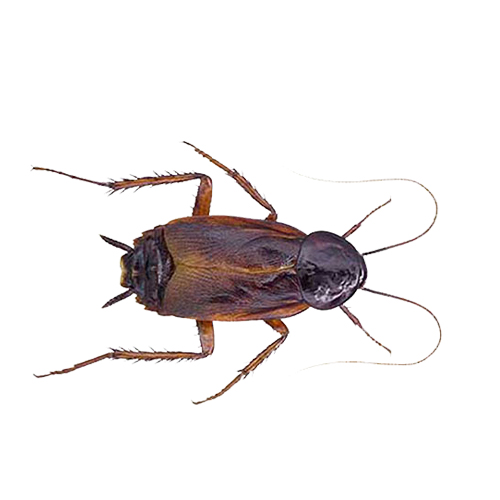

The Oriental cockroach, often called “water bugs,” prefers moist areas and cannot fly. They are slower movers compared to other roach species and thrive in damp environments.
- Scientific Name: Blatta orientalis
- Size: 1 inch long
- Appearance: Dark brown to black with a shiny, smooth body robust than other roaches. Males have short wings that cover most of their bodies, but females have shorter wing stubs or are wingless.
- Habitat: Found in cool, damp areas like basements, crawl spaces, and sewers. They can survive in outdoor areas like leaf litter and wood piles.
- Diet: Feed on decaying organic material and garbage.
8. Brown-Banded Cockroach
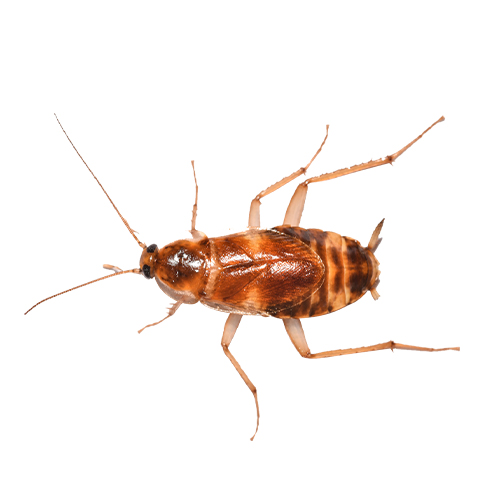

The Brown-Banded Cockroach, one of Georgia’s flying roaches, prefers higher elevations within buildings and often goes unnoticed. Unlike other species, it is less dependent on water for survival. These pests are commonly found in warm, indoor areas like ceilings and cabinets.
- Scientific Name: Supella longipalpa
- Size: 0.5 inches
- Appearance: Light brown with two distinct brown bands running across the wings and abdomen. Males have longer wings than females.
- Habitat: Prefers drier environments, such as living rooms and bedrooms. Found in high areas like ceilings, picture frames, and behind wall fixtures, inside furniture, and under appliances
- Diet: Feed on starchy materials like glue, wallpaper paste, and even book bindings.
9. Wood Cockroach
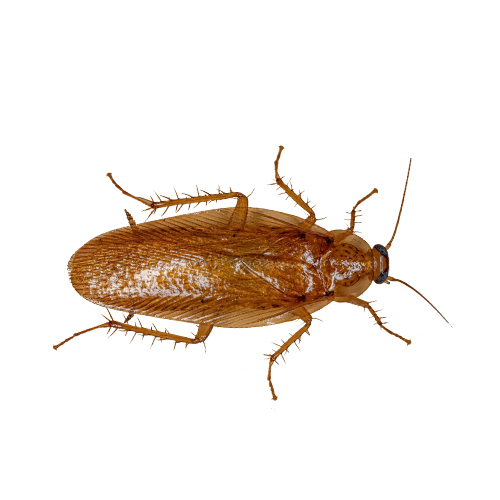

Wood roaches in Georgia are attracted to light but typically stay outdoors and are rarely a nuisance indoors. These pests thrive in wooded areas and are commonly found near decaying wood.
- Scientific Name: Parcoblatta spp.
- Size: 0.75 to 1.25 inches long
- Appearance: Light brown or tan with a slightly translucent body
- Habitat: They are found outdoors in wooded areas and under logs and occasionally enter homes but do not infest
- Diet: Feed on food scrtaps, decaying organic matter, fungi and molds on wood or leaf litter, plant-based substances, and occasionally animal matter.
How to Get Rid of Roaches in Georgia?
- Eliminate food and water sources.
- Seal cracks, gaps, and entry points.
- Declutter and maintain cleanliness.
- Use baits, traps, and insecticides.
- Consult professional pest control for severe infestations.
Take Away – Do I Need Professional Help To Get Rid of Roaches?
When it comes to cockroaches, there’s no room for compromise. These resilient pests demand expert attention to ensure complete and lasting elimination.
Don’t let them jeopardize your health, comfort, or peace of mind. Trust professionals, like Pest Force, who knows how to provide effective, tailored solutions that protect your home or business. Act now—because a pest-free environment starts with the right choice.